Terraform is an infrastructure as code (IaC) tool that allows you to create, manage, and update infrastructure resources such as virtual machines, networks, and storage in a repeatable, scalable, and automated way.
It's used for creating resources using any cloud platform that is called providers
Terraform is developed by the hashicorp.
Cloudformation is a service that is managed by the AWS(Amazon Web Service).
With Terraform, infrastructure is defined using a declarative language called HashiCorp Configuration Language (HCL) or JSON. This language allows you to describe the desired state of your infrastructure, specifying resources, their configurations, dependencies, and relationships. The Terraform configuration files define the infrastructure as code, which can be version-controlled, shared, and collaboratively developed.
What is HCL?
HCL stands for HashiCorp Configuration Language. It is the language used in Terraform for defining infrastructure configurations and resources.
HCL is a declarative language designed to be easy to read and write, allowing users to express their infrastructure requirements in a human-friendly and intuitive manner.
HCL is specifically created for managing infrastructure as code and provides a structured and concise syntax for defining resources, their configurations, and their relationships.
It enables users to describe the desired state of their infrastructure in a Terraform configuration file, which is typically named with the
.tfextension.
Task 1:
Install Terraform on your system.
follow a few steps to install Terraform on your system.
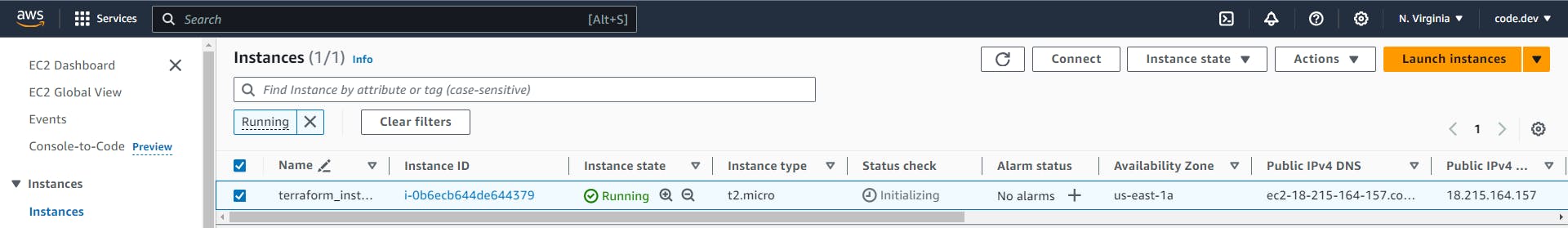
Create an EC2 instance and SSH into it.
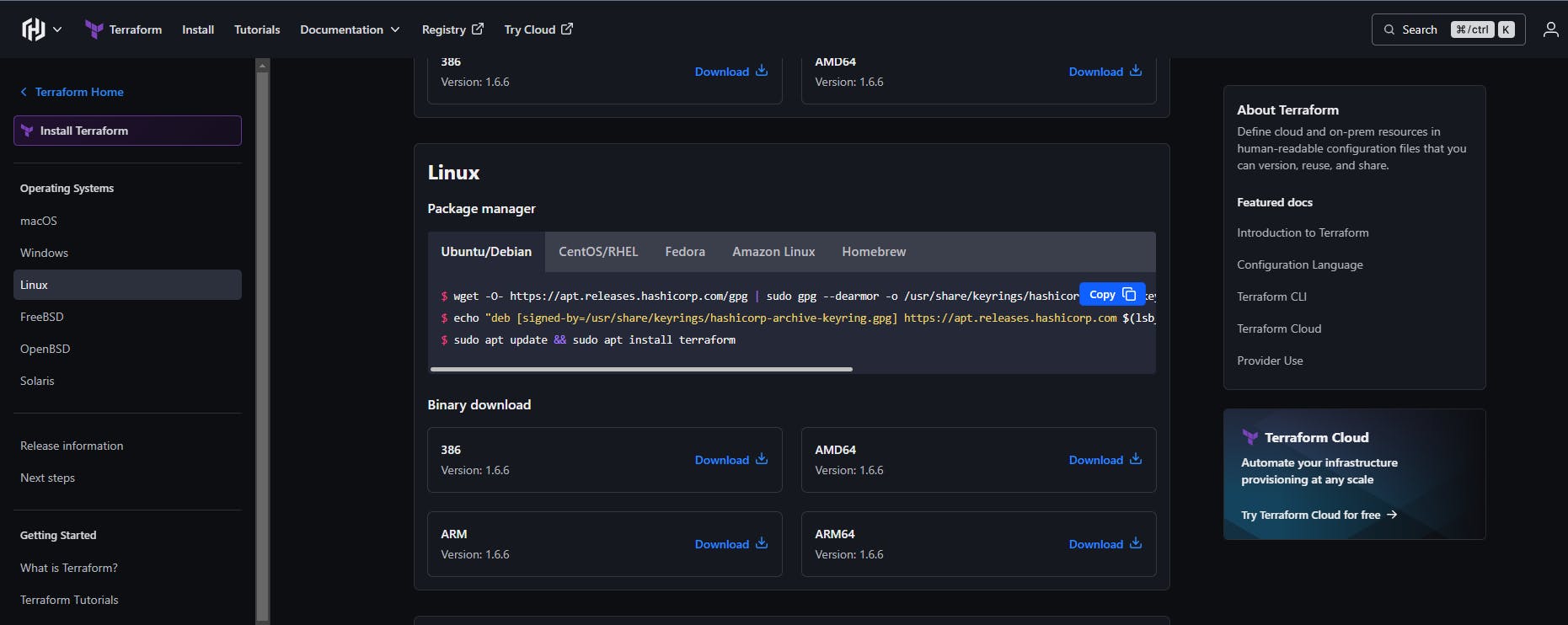
Visit the official Terraform website to get the installation step. Install Terraform
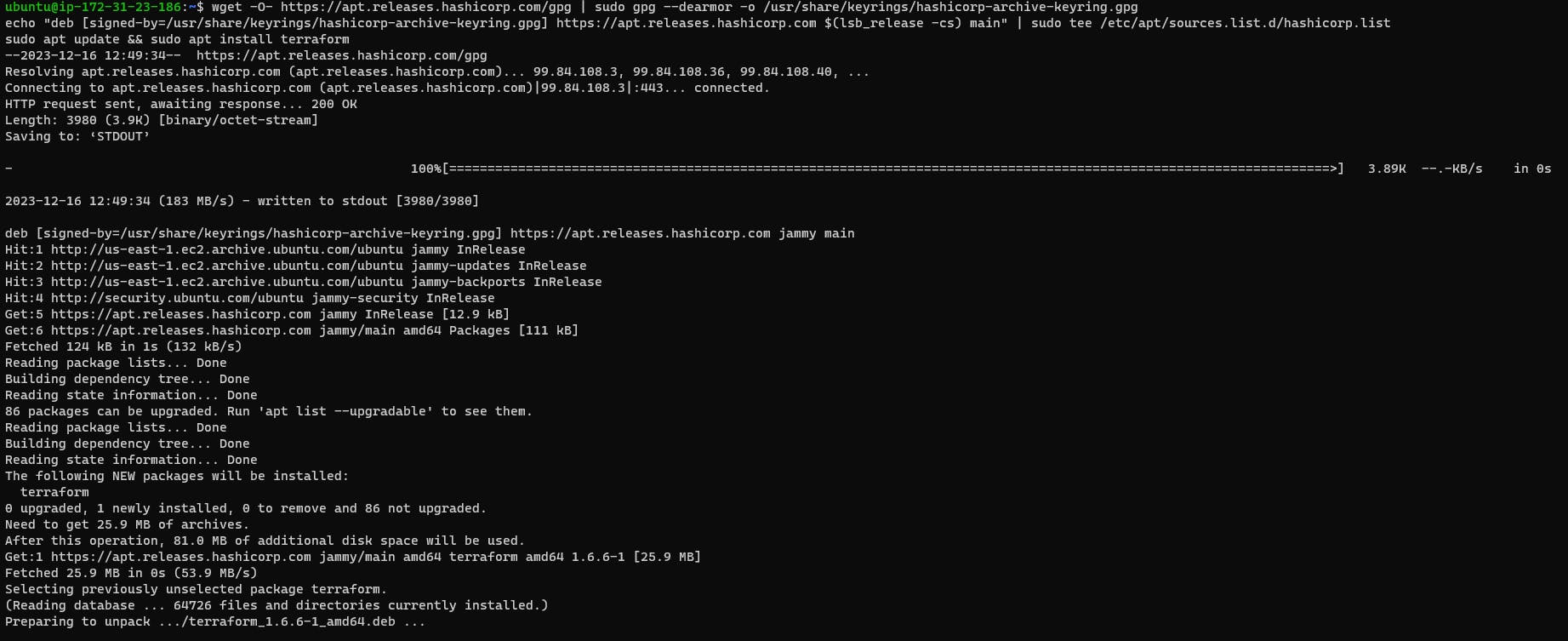
sudo apt-get update
wget -O- https://apt.releases.hashicorp.com/gpg | sudo gpg --dearmor -o /usr/share/keyrings/hashicorp-archive-keyring.gpg
echo "deb [signed-by=/usr/share/keyrings/hashicorp-archive-keyring.gpg] https://apt.releases.hashicorp.com $(lsb_release -cs) main" | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/hashicorp.list
sudo apt update && sudo apt install terraform
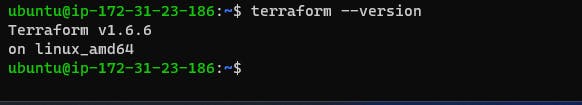
Verify that Terraform is installed correctly by running the following command:
terraform --version
Task 2: Answer the below questions
Why do we use terraform?
Terraform is a widely used open-source infrastructure as code (IaC) tool that is employed for building, changing, and versioning infrastructure efficiently. Here are some reasons why organizations and individuals use Terraform:
Infrastructure as Code (IaC): Terraform allows you to define and provision infrastructure using a declarative configuration language. This means you can describe your infrastructure as code, making it easier to version, share, and manage changes over time.
Multi-Cloud Support: Terraform supports multiple cloud providers (such as AWS, Azure, Google Cloud, and others) as well as on-premises and hybrid cloud environments. This flexibility allows users to manage infrastructure consistently across different cloud platforms.
Version Control: Infrastructure code written in Terraform can be stored in version control systems like Git. This enables teams to track changes, collaborate effectively, and roll back to previous versions if needed...
What is Infrastructure as Code (IaC)?
Infrastructure as Code (IaC) is a software engineering practice that allows the provisioning, configuration, and management of infrastructure resources through machine-readable definition files.
With Infrastructure as Code, infrastructure resources are defined using declarative or imperative code written in a domain-specific language (DSL) or a general-purpose programming language.
There are several popular tools and frameworks available for implementing Infrastructure as Code out of which Terraform is one of the popular IaC tools.
In Terraform we write the configuration file using HashiCorp Configuration Language (HCL).
What is Resource?
A resource represents a specific infrastructure object that Terraform manages. Resources can be virtual machines, databases, networks, load balancers, or any other entity offered by the cloud provider.
Each resource has a specific configuration block that defines its properties and settings.
Terraform provisions, modify or destroys resources based on their definitions.
resource "aws_instance" "my_instance"{
count = 5
ami="<ami-id>"
instance_type = "t2.micro"
tags={
Name = "terra-instance-server"
}
}
What is Provider?
A provider is a plugin in Terraform that is responsible for interacting with a specific cloud provider or service.
Providers are used to manage and provision resources within the target infrastructure. Examples of providers include AWS, Azure, Google Cloud, and more.
Each provider has its own set of resources and configuration options.
provider "aws" { region = "us-east-1" }Whats is State file in terraform? What’s the importance of it ?
The state file in Terraform is a JSON file that stores the current state of the managed infrastructure. It contains metadata about provisioned resources, their attributes, dependencies, and relationships.
The state file serves as a single source of truth for Terraform, enabling it to understand the existing infrastructure and track changes over time. It plays a crucial role in planning, applying, and destroying infrastructure.
The state file ensures idempotent operations, facilitates collaboration among team members, manages resource dependencies, and enables reproducibility.
It helps Terraform generate execution plans, validate configurations, and maintain the desired infrastructure state.
Proper management and version control of the state file is essential for maintaining consistency and ensuring accurate infrastructure management.
Backend
The backend in Terraform defines where Terraform state files are stored. This can be a local file system, remote storage services like Amazon S3 or Azure Blob Storage, or a version control system like Git.
The backend configuration determines how the state is accessed and shared among team members.
terraform { backend "remote" { organization = "example_corp" workspaces { name = "my-app-prod" } } }
What is Desired and Current State?
In Terraform, the “Desired State” refers to the configuration and settings specified in the Terraform code that describes the desired end state of the infrastructure. It represents the state you want your infrastructure to be in, such as the resources to create, modify, or delete their properties, and their relationships.
The “Current State” refers to the actual state of the infrastructure as tracked by Terraform. It is recorded in the state file and includes information about the provisioned resources, their attributes, and their dependencies. The current state reflects the real-world state of the infrastructure at any given point in time.
In this blog, we’ve delved into the realm of Infrastructure as Code (IaC) and explored the power of Terraform, accompanied by the HashiCorp Configuration Language (HCL). From understanding Terraform’s significance to mastering fundamental Terraform terms like Provider, Resource, Module, Output, State, Backend, and HCL’s core components including Blocks, Arguments, Variables, Expressions, and Interpolation, you’ve embarked on a journey to revolutionize infrastructure management. We’ve even equipped you with the skills to install Terraform on your system.
As we demystified the critical State file and its integral role in tracking and evolving infrastructure, you’ve grasped the essence of Desired and Current State, the bedrock of maintaining infrastructure as code.
Moreover, your feedback is invaluable to us. We encourage you to connect with me on LinkedIn at Akash Singh to share your thoughts, questions, or engage in further discussions. Your input plays a pivotal role in shaping our content. Join the conversation and follow my journey at #90daysofdevops to stay connected and stay informed. day60

