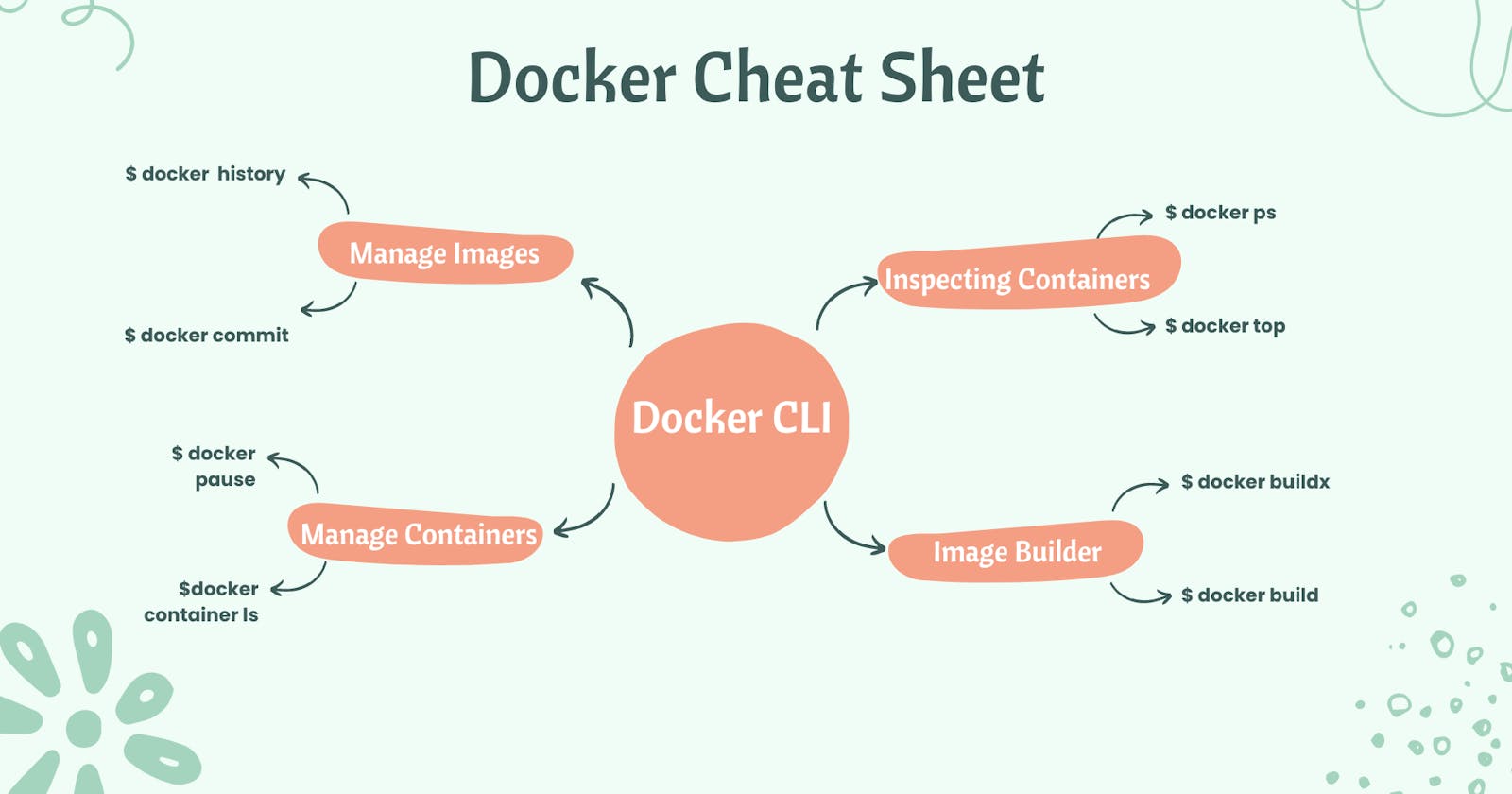
⚓🛞Docker Commands Cheat Sheet
Now that you know how Docker functions, let’s look at some of the most popular Docker command examples.
Docker installation and important commands:
Create a machine on AWS with Docker installed AMI, and install Docker if not installed.
sudo apt-get install docker.io
To see all the images present in the local machine
docker images
find the images in the docker hub.
docker search <image_name>
To download an image from the docker hub.
docker pull <image_name>
To give a name to the container and run
docker run -it --name <container-name> <image_name> /bin/bash
To check service is starting on not
service docker status
service docker info
To start the service
service docker start
systemctl docker start
To stop the service.
service docker stop
To start the container
docker start <container-name>
stop container
docker stop <container_name>
To go inside the container
docker attach <container_name>
To see all the container
docker ps -a
to see the running container
docker ps
To delete the container
docker rm <container-id>
Exit from the container
exit
To delete the images.
docker rm <image_name>
to delete all stop container
docker rm $(docker ps -a -q)
to delete multiple images
docker rmi - $(docker images -q)
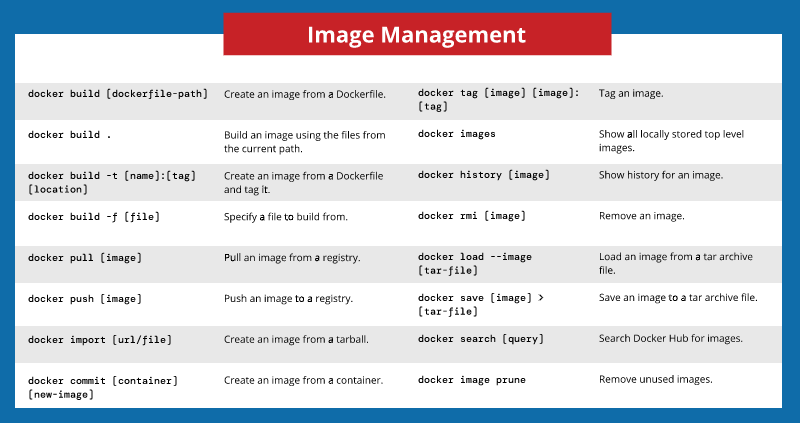
For creating images from docker file commands.
docker build . -t <image_name> {-t stands for tag}
check process state.
docker ps -a
to check the images
docker images
To create a container from the docker image
docker run -it --name <container-name> <img-name>
Create docker volume
bash image
FROM OS NAME
Volume["/myvolume"]
create an image from Dockerfile
docker build . -t <image_name>
Now create container from this image
docker run -it --name <container_name> <image_name>
Docker Volume Commands.

to see all the volumes
docker volume ls
To Create volume
docker volume create <volume_name>
To delete the volume.
docker volume rm <volume_name>
to delete all unused docker volumes
docker volume prune
To get volume details
docker volume inspect <volume_name>
To check container details
docker container inspect <container_name>
☁️Registry Commands
If you need to interact with Docker Hub, use the following commands:
Command | Explanation |
docker login | Logs in to a registry |
docker logout | Logs out from a registry |
docker pull mysql | Pulls an image from a registry |
docker push repo/ rhel-httpd:latest | Pushes an image to a registry |
docker search term | Searches Docker Hub for images with the specified term |
🌏Network Commands
If you need to interact with the Docker network, use one of the following commands:
Command | Explanation |
docker network create networkname | Creates a new network |
docker network rm networkname | Removes a specified network |
docker network ls | Lists all networks |
docker network connect networkname container | Connects a container to a network |
docker network disconnect networkname container | Disconnects a container from a network |
docker network inspect networkname | Displays detailed information about a network |
💡Conclusion:
Docker is a great tool for anyone willing to try out containers. The learning curve can be steep if you’re unfamiliar with container-based development. Luckily, having a cheat sheet at hand can speed up the process, as all common commands are easily reachable, and you don’t need to look them up on the internet.
In this tutorial, we’ve covered the basics of Docker architecture and gone through all the basic Docker commands, all of which can be found in our downloadable Docker cheat sheet.
We hope that you found this Docker tutorial useful. If you have any questions, leave them in the comments section below.
Thank you for reading!
Happy Learning 😊🙌
Thank You! Stay Connected ☁️👩💻🌈
Contact me at :
LinkedIn: Akash Singh